AbDesign
Database
Database of point mutants of antibodies with associated structures reveals poor generalization of binding predictions from machine learning models
Learn moreIntroduction
Antibodies are crucial tools in therapeutic, diagnostic, and research applications. To enable advancements in antibody design and optimization, we present AbDesign DB — a curated dataset of antibody-antigen complexes, each paired with detailed mutational data. This resource is intended for computational/machine learning antibody engineers.
AbDesign DB provides a large, experimentally consistent dataset for studying the effects of single-point mutations on antibody binding. Our dataset addresses key challenges such as the limited availability of structural and affinity data and the inconsistency in experimental conditions across studies.
14
antibody-antigen complexes:
Each structure derived from 7 antigens paired with two distinct antibodies.
658
point mutations: Targeted to CDR-H3 residues within 4.5Å of antigen heavy atoms.
Structural Models
High-resolution wild-type structures and mutant models, generated with computational refinement.
Binding Data
ELISA measurements for all variants, normalized against their respective wild-type binding.
Supplementary data: single point mutants from AB-Bind and SKEMPIv2 for completeness.
Accessing the Database
We make the AbDesign DB free for non-commercial use by non-commercial entities. If you are a commercial entity and would like to employ the data in your activities, please get in touch with us.
We claim absolutely no rights to the SKEMPI and AB-Bind datasets.
Data format
The AbDesign DB dataset is available in formats tailored for easy integration into various workflows:
Sequence Data: Mutational details include positions, amino acid substitutions, and ELISA binding ratios.
Structural Data: Coordinates for wild-type and mutant antibodies are provided in standard PDB format.
Directory structure
The data is structured into following directories:
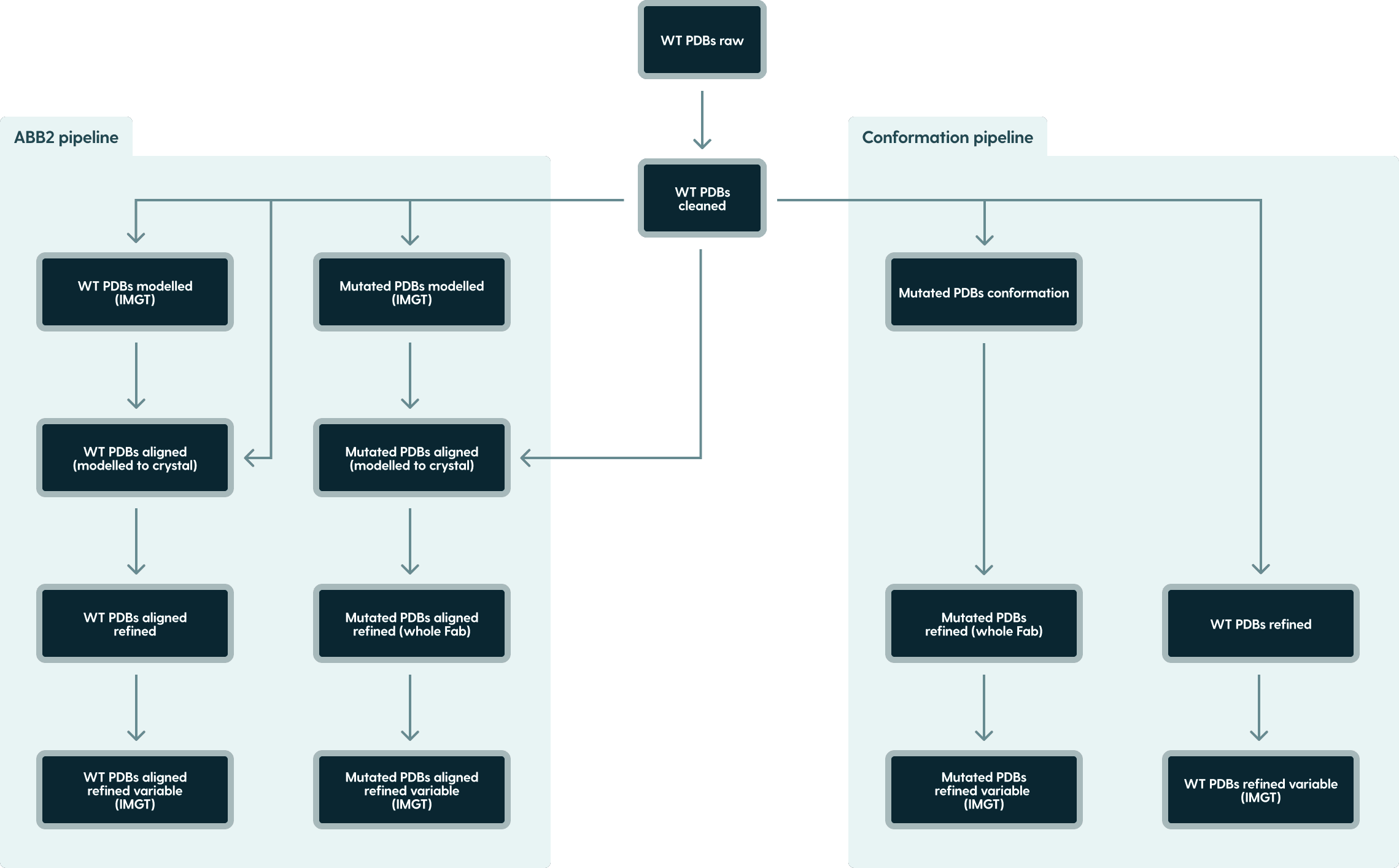
Figure 1. PDB dataset directory structure.
Example Data Entry
Each data entry includes comprehensive metadata, binding results, and structural details. For instance:
Column name
Value
index
0
original_id
<empty>
dataset
AbDesign
pdb_name
1BJ1
method
ELISA
affinity
0.885605
affinity_type
H
mutation_chain_id
H
orig_residue
H
mutation_pos
101
mutation_pos_imgt
109
mutation_pos_imgt_wt
109
new_residue
Y
mutated_pdb_name
0__1BJ1__H_101_H_Y.pdb
mutated_pdb_name_imgt
0__1BJ1__H_109_H_Y.pdb
orig_antigen_chain_id
W
orig_heavy_chain_id
H
orig_light_chain_id
L
antigen_sequence
VVKFMDVYQRSYCHPIETLVDIFQEYPDEIEYIFKPSCVPLMRCGG...
heavy_sequence
EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGYTFTNYGMNWVRQAPLE...
light_sequence
DIQMTQSPSSLSASVGDRVTITCSASQDISNYLNWYQQKPGKAPK...
heavy_sequence_variable
EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGYTFTNYGMNWVRQAPGK...
heavy_cdr1
GYTFTNYG
heavy_cdr2
INTYTGEP
heavy_cdr3
AKYPYYYGSSHWYFDV
heavy_variable_start
0
heavy_variable_end
123
heavy_imgt_to_residue_ma...
{'1': 'E', '2': 'V', '3': 'Q', '4': 'L', '5': ...}
heavy_positional_imgt_map...
{0: '1', 1: '2', 2: '3', 3: '4', 4: '5', 5: '6...}
light_sequence_variable
DIQMTQSPSSLSASVGDRVTITCSASQDISNYLNWYQQKPGKAP...
light_cdr1
QDISNY
light_cdr2
FTS
light_cdr3
QQYSTVPWT
light_variable_start
0
light_variable_end
107
light_imgt_to_residue_mapp...
{'1': 'D', '2': 'I', '3': 'Q', '4': 'M', '5': ...}
light_positional_imgt_mappi...
{0: '1', 1: '2', 2: '3', 3: '4', 4: '5', 5: '6...}
Index: Index of the mutation in the particular dataset.
Original ID: Columns taken from original datasets - PDB name and chain IDs concatenated with mutation string.
For SKEMPIv2: <#Pdb>_<Mutation(s)_cleaned>
For AB-Bind: <#PDB>_<Partners(A_B)>_<Mutation>
For AbDesign: empty stringDataset: The name of the dataset this mutation belongs to.
PDB Name: The name of the PDB file for the wild-type structure.
Method: Experimental method used to determine the affinity.
Affinity: The measured affinity value for the antibody-antigen interaction.
Affinity Type: The type of affinity measurement (ELISA / ∆∆G).
Mutation Chain ID: The chain ID where the mutation occurs (H for heavy, L for light).
Orig Residue: The original (wild-type) residue at the mutation site.
Mutation Pos: The position of the mutation in the original numbering scheme.
Mutation Pos IMGT: The position of the mutation in the IMGT numbering scheme.
Mutation Pos IMGT WT: The IMGT position of the mutation in the wild-type structure ( NOTE: Some mutations result in the different IMGT numbering of mutated sequence, when compared to WT sequence. This column points to the mutation site in IMGT numbered WT structures - _modelled and _variable directories.)
New Residue: The new (mutated) residue.
Mutated PDB Name: The name of the PDB file for the mutated structure. The name follows convention:
104__1N8Z__H_52_Y_A.pdb
<Index>__<PDB name>__<Mutation Chain>_<Mutation Pos>_<Orig Residue>_<New Residue>.pdb
Where:
104 is the mutation identifier
1N8Z is the original PDB ID
H is the chain where the mutation occurs (heavy chain)
52 is the residue number of the mutation site
Y is the original residue (tyrosine)
A is new residue (alanine)Mutated PDB Name IMGT: The name of the PDB file for the mutated structure with IMGT numbering. Follows the same convention as Mutated PDB Name, but uses Mutation Pos IMGT instead of Mutation Pos.
Orig Antigen Chain ID: The chain ID of the antigen in the original structure.
Orig Heavy Chain ID: The chain ID of the heavy chain in the original structure.
Orig Light Chain ID: The chain ID of the light chain in the original structure.
Antigen Sequence: The amino acid sequence of the antigen.
Heavy Sequence: The full amino acid sequence of the heavy chain.
Light Sequence: The full amino acid sequence of the light chain.
Heavy Sequence Variable: The amino acid sequence of the variable region of the heavy chain.
Heavy CDR1: The sequence of the first complementarity-determining region (CDR) of the heavy chain.
Heavy CDR2: The sequence of the second CDR of the heavy chain.
Heavy CDR3: The sequence of the third CDR of the heavy chain.
Heavy Variable Start: The starting position of the variable region in the heavy chain. (0-based)
Heavy Variable End: The ending position of the variable region in the heavy chain. (0-based exclusive)
Heavy IMGT To Residue Mapping: Mapping between IMGT positions and residues for the heavy chain.
Heavy Positional IMGT Mapping: Mapping of sequence index positions to IMGT numbering for the heavy chain.
Light Sequence Variable: The amino acid sequence of the variable region of the light chain.
Light CDR1: The sequence of the first CDR of the light chain.
Light CDR2: The sequence of the second CDR of the light chain.
Light CDR3: The sequence of the third CDR of the light chain.
Light Variable Start: The starting position of the variable region in the light chain.
Light Variable End: The ending position of the variable region in the light chain.
Light IMGT To Residue Mapping: Mapping between IMGT positions and residues for the light chain.
Light Positional IMGT Mapping: Mapping of sequence index positions to IMGT numbering for the light chain.
Accessing the Database
We make the AbDesign DB free for non-commercial use by non-commercial entities. If you are a commercial entity and would like to employ the data in your activities, please get in touch with us.
We claim absolutely no rights to the SKEMPI and AB-Bind datasets.
Citing this work
The dataset and associated study are described in this manuscript, please cite it if you use the data:
AbDesign: Database of point mutants of antibodies with associated structures reveals poor generalization of binding predictions from machine learning models
Since for convenience we included the SKEMPI and AB-Bind datasets please cite their papers when using this work:
SKEMPI 2.0: an updated benchmark of changes in protein–protein binding energy, kinetics and thermodynamics upon mutation.
Authors: Jankauskaitė, Justina, et al
Journal: Bioinformatics 35.3 (2019): 462-469.
AB‐bind: antibody binding mutational database for computational affinity predictions.
Authors: Sirin, Sarah, et al.
Journal: Protein Science 25.2 (2016): 393-409.